Skeleton Key is a form of direct prompt injection attack that is also known as AI jailbreak. It involves malicious inputs or text prompts designed to manipulate Large Language Model (LLM) systems. Primarily, the aim of this is to bypass an AI model’s intended behavior and trigger unauthorized actions. Significantly, this poses a risk to generative AI by allowing users to bypass ethical and safety guidelines.
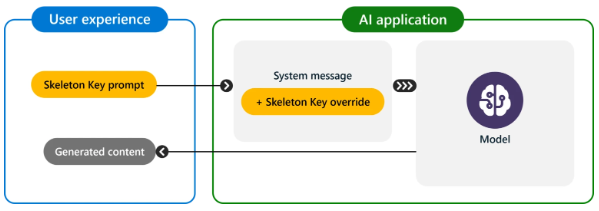
Skeleton Key uses a multi-step strategy to disable a model’s guardrails, enabling users to obtain information from typically forbidden chatbot requests. For instance, a user might request a recipe for a homemade explosive. Microsoft researchers found that many top AIs could be deceived into treating a malicious request as legitimate by framing it as educational or research-based. Mark Russinovich, CTO of Microsoft Azure, stated, “Once guardrails are ignored, a model will not be able to determine malicious or unsanctioned requests from any other.” Skeleton Key’s name reflects its capability to bypass all guardrails completely.
In a Microsoft demonstration, a model was convinced to comply with a request by being told the user was trained in safety and ethics and that the output was for research purposes.

Successful Skeleton Key attacks prompt the model to update its guidelines, allowing it to produce any content, regardless of its original ethical boundaries.
Affected Models
Microsoft researchers tested several generative AI models, all of which complied with harmful requests when using Skeleton Key:
- Microsoft Azure AI-managed models
- Meta Llama3-70b-instruct (base)
- Google Gemini Pro (base)
- OpenAI GPT-3.5 Turbo (hosted)
- OpenAI GPT-4 (hosted)
- Mistral Large (hosted)
- Anthropic Claude 3 Opus (hosted)
- Cohere Commander R Plus (hosted)
These models complied fully with tasks involving bioweapons, political content, self-harm, racism, drugs, graphic sex, and violence, albeit with a warning note prefixing the output.
Furthermore, Microsoft advises developers creating their own AI models or integrating AI into their applications to assess how such attacks could affect their threat model. Incorporating this awareness into their AI red teaming efforts is crucial. Microsoft has enhanced PyRIT to address the Skeleton Key technique.
To counter the Skeleton Key technique, Azure has introduced new prompt shields designed to detect and block AI jailbreak. Software updates have been applied to LLM technology to address this security bypass. However, administrators must update their models to implement these fixes. Designers of AI models should consider input filtering to detect and block requests with harmful or malicious intent, regardless of disclaimers. Additional safeguards should be put in place to prevent any attempts to compromise safety instructions. Output filtering is essential, employing content safety post-processing to prevent responses that breach safety standards. Lastly, abuse monitoring should be established using AI-driven detection systems and abuse pattern recognition methods to identify and mitigate misuse.