Imagine a cybercriminal locking your computer and demanding money to unlock it. That’s how ransomware works, and the rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is playing a huge role in a recent trend called Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS). RaaS is a subscription-based ransomware model that makes it easy for attackers to launch these attacks.
RaaS Makes Ransomware a Booming Business
Cybercriminal groups such as DarkSide, REvil, etc. develop and maintain ransomware tools. Then, instead of directly attacking victims themselves, they rent or sell access to these tools to those who want to extort victims through cyberattacks. This RaaS model often includes additional features like marketing and customer support to advertise their services and offer help to customers who purchase access to their ransomware tools, and negotiation assistance to help negotiate ransoms with victims.
This “all-in-one” approach makes it easier for inexperienced cyber criminals, making ransomware attacks a much bigger threat for businesses and individuals alike. A report by Check Point Research shows 1 in 10 organizations globally, got hit by ransomware in 2023.
A Visual Overview of how RaaS Work
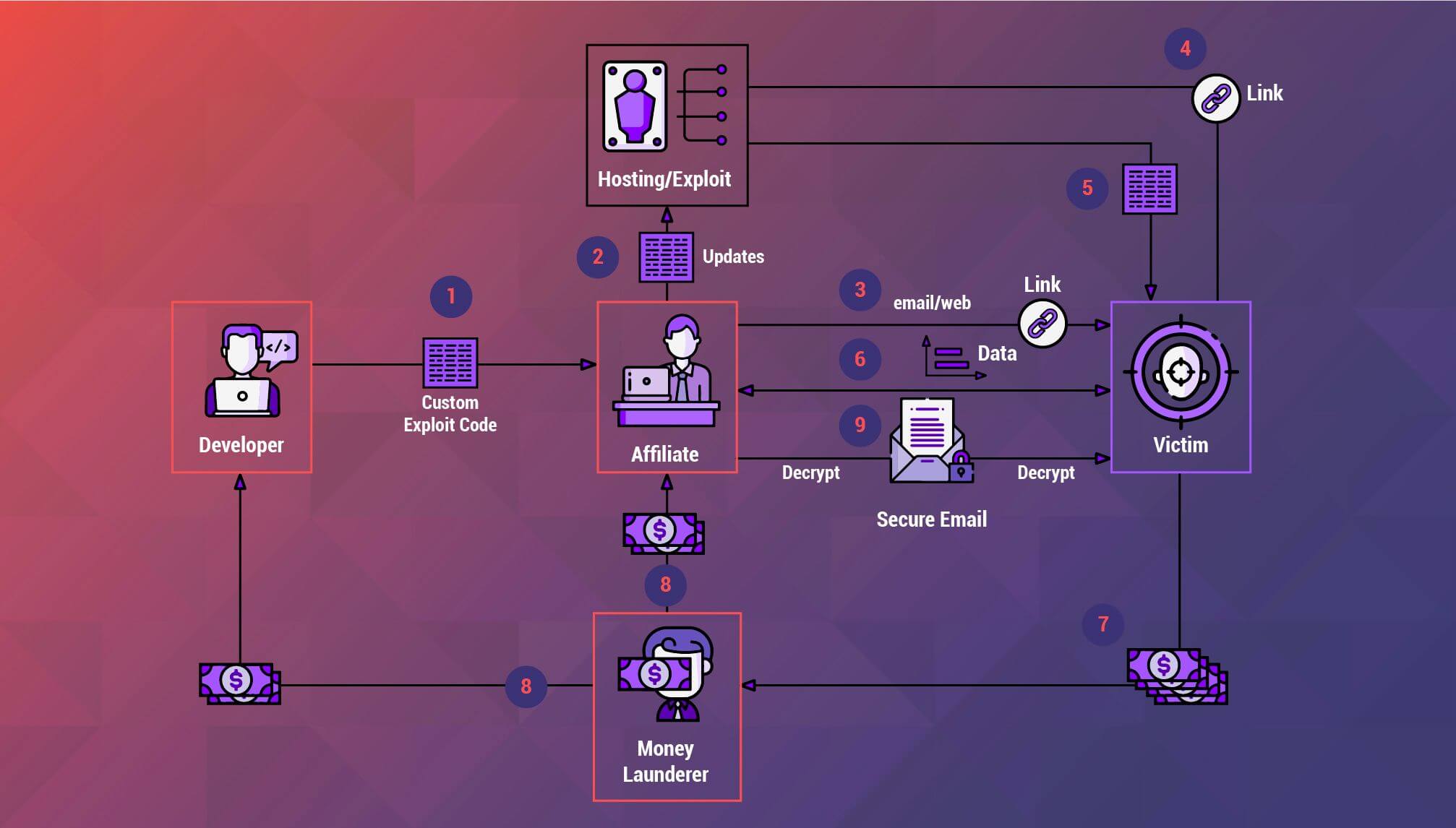
Credit: Appknox
AI: The Double-Edged Sword
While AI can be used by security analysts to develop advanced defenses, threat actors are also leveraging it to automate tasks and improve the efficiency of cyber-attacks. According to the UK’s National Cyber Security Center (NCSC), ransomware actors are already using AI to increase the speed and effectiveness of existing attack methods, such as reconnaissance, phishing, and coding. This trend will almost certainly continue making cyberattacks a growing threat.
How AI is fueling ransomware attacks:
- Automated Targeting: AI can be used to identify and target vulnerable systems. For instance, attackers might use AI to scan for specific software vulnerabilities or exploit weak passwords.
- Social Engineering: AI-powered bots can be used to create personalized phishing emails or conduct social media scams, tricking victims into clicking malicious links or downloading malware.
- Evasion Techniques: AI can help attackers develop ransomware that bypass traditional security measures.
- Ransomware Negotiator: There have already been cases where threat actors have asked for assistance from ChatGPT during ransomware negotiations. AI-powered chatbots could serve as future ransomware intermediaries and be trained to respond based on victim behavior.
What Can Businesses Do?
Some proactive cybersecurity measures businesses can take:
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date on the latest cyber threats and vulnerabilities using the National Cyber Security Centre’s ransomware and cyber security hygiene advice to strengthen their defenses and boost their resilience to cyberattacks.
- Patch Systems Regularly: Apply security patches promptly to address software vulnerabilities that attackers might exploit.
- Invest in Security Awareness Training: Train employees on how to identify and avoid phishing attempts and other social engineering tactics.
- Have a Backup and Recovery Plan: In case of a ransomware attack, having a backup and recovery plan is crucial for minimizing downtime and data loss.
The Future of RaaS
With the advancement of AI, the potential harm that cybercriminals can cause has increased severely. According to cybersecurity experts, RaaS Is not going to go away any time soon. The ease of launching attacks and the potential financial gain make it a lucrative business for criminals. However, the advancements in AI are also leading to the development of more effective cybersecurity solutions to ensure businesses are active round the clock to prevent the risk of RaaS.





