This article explores key cybersecurity areas where AI is making a significant impact and looks into leading AI-powered tools from various vendors.
Why AI in Cybersecurity?
The answer is simple: attackers are already leveraging AI to enhance their tactics. Therefore, cybersecurity professionals can utilize AI to become more efficient and effective. AI steps in to bridge the gap by offering:
Superior Data Analysis: AI excels at analyzing vast quantities of data from endpoints, networks, and applications. This allows for superior threat detection and anomaly identification compared to human analysts.
Automation and Efficiency: AI automates repetitive tasks, freeing up security professionals to focus on strategic initiatives. Additionally, it streamlines workflows and information retrieval, boosting overall efficiency.
Continuous Learning: AI models continuously learn and adapt to new threats. This ensures your defenses remain effective against the latest attack vectors and emerging malware.
AI in Action: Addressing Cybersecurity Challenges
Let’s look at how AI solves specific cybersecurity challenges across nine domains and explore some leading AI-powered vendor tools:
1. Automated Incident Response
This involves automating the detection, containment, and eradication of security incidents.
Challenge: Incident response is a time-sensitive process requiring a skilled team to contain threats, eradicate them, and restore affected systems.
AI Solution: AI can analyze security logs, identify suspicious activity in real-time, and orchestrate automated responses to contain threats. Eg.
Microsoft Security Copilot is a frontrunner in AI-powered incident response. It analyzes complex security events and identifies sophisticated threats that might evade traditional security tools.
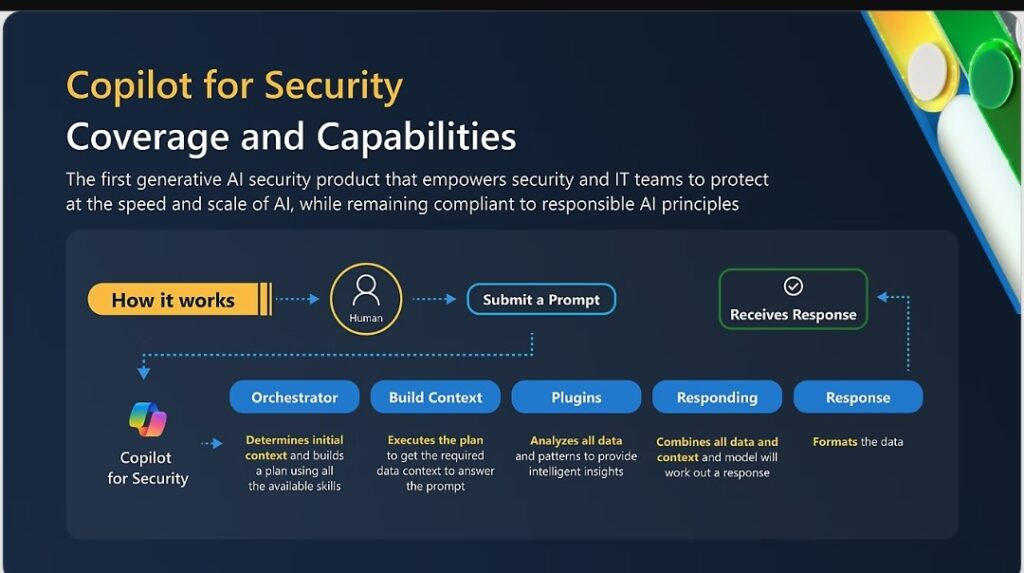
Darktrace is another noteworthy tool, it continuously learns and adapts as it encounters new data, utilizing an AI-driven feedback loop to protect data from sophisticated cyberattacks.
2. Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
DLP safeguards sensitive data from unauthorized access or exfiltration.
Challenge: Protecting sensitive data (PII, financial data, intellectual property) from unauthorized access or exfiltration is a complex task.
AI Solution: AI can analyze data flows, identify anomalies that might indicate a breach, and prevent sensitive data from being transferred to unauthorized locations. Eg.
Nightfall AI offers another approach, employing Natural Language Processing (NLP) to analyze documents and emails for sensitive data identification.
Zscaler Data Protection utilizes AI to classify data at scale, providing visibility into sensitive information location and its risk of exposure.
3. Malware Analysis and Reverse Engineering
This involves understanding how malicious software (malware) works to build better defenses to stop it and even shut it down completely.
Challenge: Manually analyzing vast amounts of malware samples is time-consuming and resource-intensive.
AI Solution: AI can automate the analysis of suspicious code, identify patterns in malware behavior, and even predict future attacks. Eg.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security is a comprehensive security suite designed to protect businesses and organizations from cyber threats. It leverages AI and machine learning to offer functionalities like AI-powered malware detection, targeted attack prevention, and impact on system performance.
Malwarebytes is a security software program known for its ability to detect and remove malware, including ransomware, spyware, and adware. its capabilities include AI-powered malware detection, real-time threat detection, and proactive threat hunting.
RevEng.AI uses a deep learning AI model called BinNet to analyze binary computer code, specifically focused on reverse engineering and malware analysis. It assists security professionals in understanding and dissecting executable binaries.
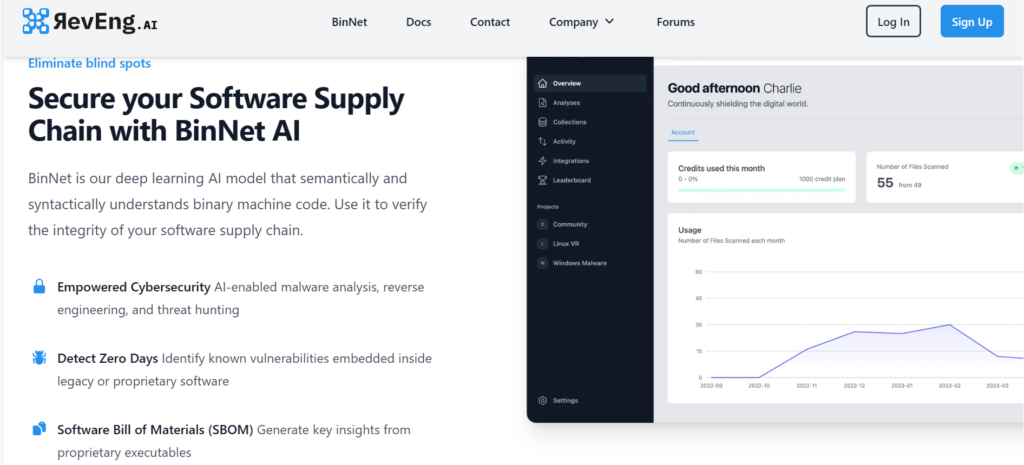
4. Risk Assessment
This is the process of identifying, evaluating, and prioritizing cybersecurity risks.
Challenge: Assessing potential risks and vulnerabilities requires both technical knowledge and a deep understanding of an organization’s business processes.
AI Solution: AI can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and trends that indicate potential threats, allowing for more focused risk mitigation strategies. Eg.
IBM’s Guardium analyzes massive amounts of data collected from various sources within your network and provides insights into the potential business impact of each vulnerability, allowing for prioritization based on risk.
Tenable’s Exposure AI utilizes AI to automate the process of discovering and understanding all the assets within your network that could be potential attack points. It also analyzes the context of each vulnerability and its potential exploitability, helping prioritize which ones to address first.
5. Threat Detection and Prevention
This involves identifying and stopping cyber threats before they can cause damage.
Challenge: Identifying threats and anomalous behavior indicative of malicious activity within vast data sets is a significant challenge.
AI Solution: AI can analyze network traffic, user behavior, and other data sources to detect threats with higher accuracy and speed. Eg.
Tessian provides a complete Cloud Email Security platform that leverages AI to prevent phishing attacks, business email compromise (BEC) and protect sensitive email data.
Microsoft Security Copilot utilizes AI to analyze data, detect threats, and automate tasks like investigation, containment, and remediation of email-related security incidents.
6. Vulnerability Scanning and Patch Management
This involves regularly scanning systems for vulnerabilities and applying security patches to address them.
Challenge: Traditionally, vulnerability scanning and patch management are time-consuming processes, leaving vulnerable software exposed for extended periods.
AI Solution: AI can automate vulnerability scanning, prioritize vulnerabilities based on potential risks, and even automate patch deployment in some cases. Eg.
IBM’s Guardium adapts to threat landscapes by identifying new patterns and threats, ensuring data security across on-premises and cloud environments.
Tenable’s Exposure AI identifies all potential access points within a network, prioritizes vulnerabilities, and utilizes predictive analysis to identify software susceptible to future attacks.
7. Threat Hunting
This is the proactive search for hidden threats within a network.
Challenge: Sifting through massive data sets from various sources to uncover signs of malicious activity.
AI Solution: AI can analyze network data for subtle indicators of compromise (IOCs) that might be missed by traditional security tools. Eg.
SentinelOne Singularity Analyzes endpoint data for anomalies and suspicious activities. It also Identifies malware and advanced threats attempting to infiltrate devices and automates response actions to contain threats and minimize damage

IBM QRadar Security and Event Management (SIEM) utilizes AI to analyze vast amounts of security data from endpoints, networks, and servers. By identifying anomalies and suspicious patterns, these tools can help you uncover hidden threats before they cause damage.
8. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM ensures that only authorized users have access to specific systems and data.
Challenge: Traditional IAM systems require constant monitoring for access anomalies.
AI Solution: AI can learn user behavior patterns and detect anomalies that might indicate unauthorized access attempts. Eg.
IBM Verify employs AI for access control by analyzing user behavior with behavioral biometrics. This enables dynamic authentication adjustments based on detected anomalies.
9. Penetration Testing and Ethical Hacking
Ethical hackers simulate cyberattacks to identify vulnerabilities in a system’s defenses.
Challenge: Testing large IT environments or complex applications can be time-consuming and require specialized knowledge.
AI Solution: AI can automate penetration testing tools, conduct complex simulations, and prioritize the most critical vulnerabilities to address. Eg.
Tenable’s Exposure AI utilizes AI for vulnerability scanning, automating the process of identifying weaknesses in systems. WhilemTenable’s Exposure AI leverages AI for vulnerability scanning, future advancements might see Burp Suite extensions incorporating AI to bridge the knowledge gap for unfamiliar systems.
Conclusion
By leveraging these AI-powered tools, organizations can build a robust and future-proof security posture. However, it’s important to acknowledge that AI security solutions, like any technology, have limitations. Future advancements will likely address these limitations and further enhance the AI security landscape.




