In a concerning development, a new AI-powered phishing campaign has targeted Gmail’s 2.5 billion users, marking a significant leap in the sophistication of cyber threats. The attack exploited advanced AI techniques to bypass traditional security measures. This incident highlights the need for user awareness and advanced security measures.
The recent phishing campaign involved the use of AI-generated voice deepfakes, introducing a new layer of deception in social engineering tactics. One notable victim, Sam Mitrovic, a Microsoft solutions consultant, narrowly avoided being tricked by a “super realistic AI scam call.” The attack began with a routine-looking Gmail account recovery request, followed by a phone call from a U.S. number. After ignoring a similar attempt a week earlier, Mitrovic answered the call this time. The caller, posing as a Google support agent, used an AI-generated voice to sound convincingly authentic, creating the illusion that his account had been compromised.
The scam exploited legitimate Google support protocols, referencing Mitrovic’s recent account activity and suggesting unauthorized logins from foreign locations to instill a sense of urgency. This tactic made the request for immediate action appear genuine. However, Mitrovic’s skepticism prompted him to investigate the phone number, which turned out to be listed on authentic Google business pages—further lowering his suspicion.
Deepfake Voices and AI in Phishing
The use of AI-generated voices in phishing scams is rapidly becoming a significant threat. These schemes extend beyond traditional email phishing to include vishing, where attackers deploy AI to replicate human speech convincingly. The AI-generated voice in this incident responded to conversational pauses with near-perfect timing, raising subtle but crucial red flags.
In another high-profile case, Y Combinator founder Garry Tan encountered a similar AI-enhanced scam.
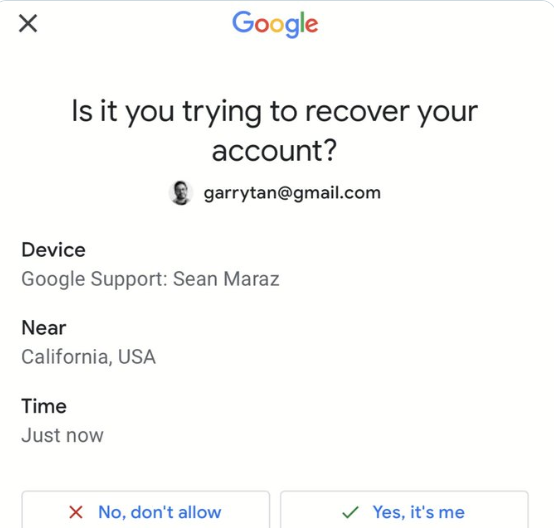
The caller falsely claimed that Google had received a death certificate and that a family member was attempting to access his account. The goal was to manipulate Tan into authorizing a password reset, showcasing the lengths to which attackers are willing to go, and how AI is being used to weave elaborate and urgent narratives.
Google’s Response
In light of the growing threat, Google has launched the Global Signal Exchange, a collaborative initiative with the Global Anti-Scam Alliance (GASA) and the DNS Research Federation. The program aims to disrupt scam networks by sharing real-time intelligence on phishing tactics and malicious activity. During its pilot phase, the initiative has already processed millions of scam-related signals and flagged over 100,000 malicious URLs, leveraging AI on Google Cloud for real-time analysis.
Additionally, Google has updated its Advanced Protection Program (APP) to include passkey support, enhancing security for high-risk users such as journalists and politicians. The APP combines hardware-based authentication with biometrics to provide a robust defense mechanism, ensuring that even if login credentials are compromised, attackers cannot access the account without the user’s physical device and biometric confirmation. The program also limits third-party app access to Gmail data, reducing the potential attack surface.
Staying Safe from AI-Powered Phishing Scams
To combat the threat of AI-driven phishing, Gmail users should follow these best practices:
- Google will never call or email users unexpectedly to confirm account recovery or address suspicious activity. Verify any requests through official channels before taking action.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) and consider enrolling in the Advanced Protection Program for added security.
- If you receive a suspicious call or email, avoid rushing to respond. Verify the legitimacy by checking recent Gmail activity for unusual logins and researching the contact information provided.
- AI-generated voices often have subtle giveaways, such as overly consistent speech patterns and perfectly timed pauses. Being aware of these can help identify fraudulent calls.
- Never provide personal details or make account changes based solely on a phone call. If unsure, hang up and reach out to Google support directly through verified contact details.
Conclusion
The rise of AI-powered phishing attacks marks a critical turning point in cybersecurity, where sophisticated technologies enable cybercriminals to deploy more convincing social engineering tactics. Google’s initiatives, such as the Global Signal Exchange and the Advanced Protection Program, aim to stay ahead of these threats. However, the most crucial defense remains user awareness.





