A critical vulnerability was discovered within Red Hat’s OpenShift AI and OpenShift Data Science platforms. Specifically, The vulnerability, CVE-2024-7557, allows attackers to bypass authentication and escalate privileges across AI models within the same namespace.
Notably, OpenShift AI and Data Science platforms are integral to many organizations deploying artificial intelligence (AI) solutions. It provides a cloud-based environment for developing and managing AI models. Importantly, these platforms enable users to deploy intelligent models, for data analysis, machine learning, and automated decision-making processes.
Moreover, researchers found the CVE-2024-7557 vulnerability in how OpenShift handles ServiceAccount tokens, which authenticate and authorize interactions with Kubernetes resources. Specifically, attackers could exploit credentials assigned to one AI model to gain access to other models and APIs within the same namespace.
By leveraging these tokens, an attacker could execute the oc --token={token} command, allowing them to move laterally within the namespace and potentially access sensitive data and resources. The compromised ServiceAccount tokens, visible in the user interface, allowed unauthorized access across models, thereby threatening the security and integrity of these systems.
Server-side vulnerabilities like this are particularly dangerous because they exploit internal mechanisms that often go unchecked. Consequently, the CVSS v3.1 score of 7.6 reflects the vulnerability’s high impact on confidentiality, integrity, and availability. The scoring also emphasizes that attackers can exploit this flaw with low complexity and without user interaction, making it a significant threat to affected systems.
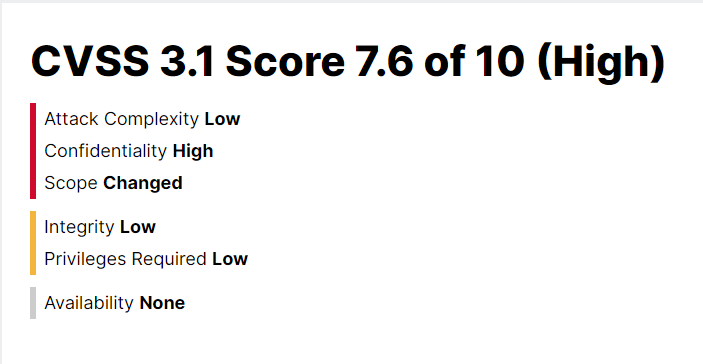
Currently, Red Hat has not detailed any specific remediation. However, organizations using OpenShift AI should actively monitor for updates and promptly apply patches as they become available.
Futhermore, it’s critical for affected organizations to reassess their access controls. This ensures that ServiceAccount tokens are appropriately managed and that lateral movement within namespaces is restricted. Additionally, Implementing additional layers of security, like IDS and regular audits, can help mitigate the risk of exploitation.
The Openshift AI vulnerability highlights the challenges in securing AI-powered platforms. As these technologies become more integrated into critical operations, the need for security practices grows ever more apparent.





