Traditional threat intelligence approaches, which were once the foundation of cybersecurity policies are progressively failing due to the continuously changing threat landscape. The amount and complexity of emerging cyber threats have overloaded traditional methodologies, leaving them quite inefficient in generating timely insights. This is where CensysGPT comes in.
About CensysGPT
CensysGPT is an advanced AI-powered tool developed by Censys. It is fundamentally used to simplify and enhance the process of network reconnaissance and security analysis.
CensysGPT leverages the capabilities of OpenAI’s GPT technology. It allows users to create search queries in natural language. This significantly reduces the complexity typically associated with writing precise search queries in Censys’s query language.
How to use CensysGPT
Using CensysGPT begins with inputting your natural language. The term “natural language” describes the spoken or written words that people use to communicate with one another. Examples of natural languages include English, Spanish, Mandarin, Swahili, and thousands of others spoken around the world.
The conversion of natural language to Censys search queries is the intriguing thing about CensysGPT. The following images show the use of CensysGPT
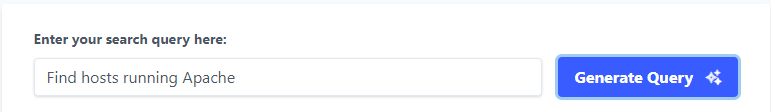
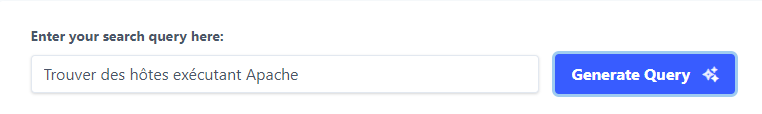
After inputting the natural language for your request and clicking on “Generate Query”, CensysGPT generates the Censys query for your request as seen below.
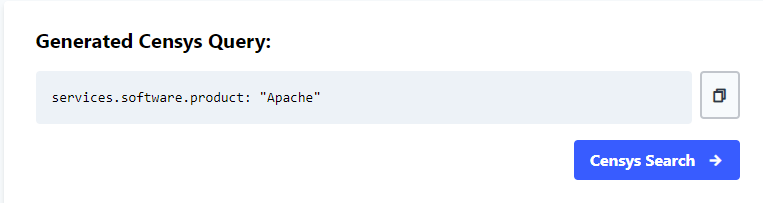
With this, you can proceed to carry out your Censys search.
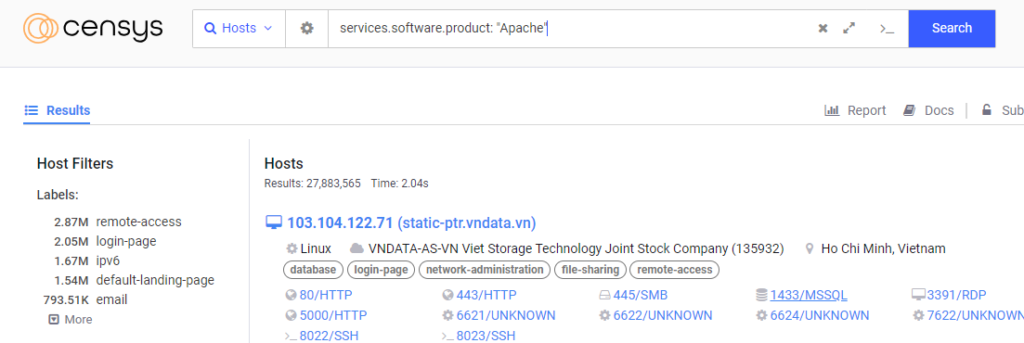
The image above is the result of the query generated by censysGPT.
For further insight on how to use CensysGPT, watch this:
Conclusion
As CensysGPT is still in beta, users are welcome to offer suggestions for how to make the tool better. Its purpose is to simplify the process of identifying vulnerabilities, analyzing network patterns, and threat intelligence, making it an invaluable tool for security researchers, IT professionals, and anyone else interested in cybersecurity.





